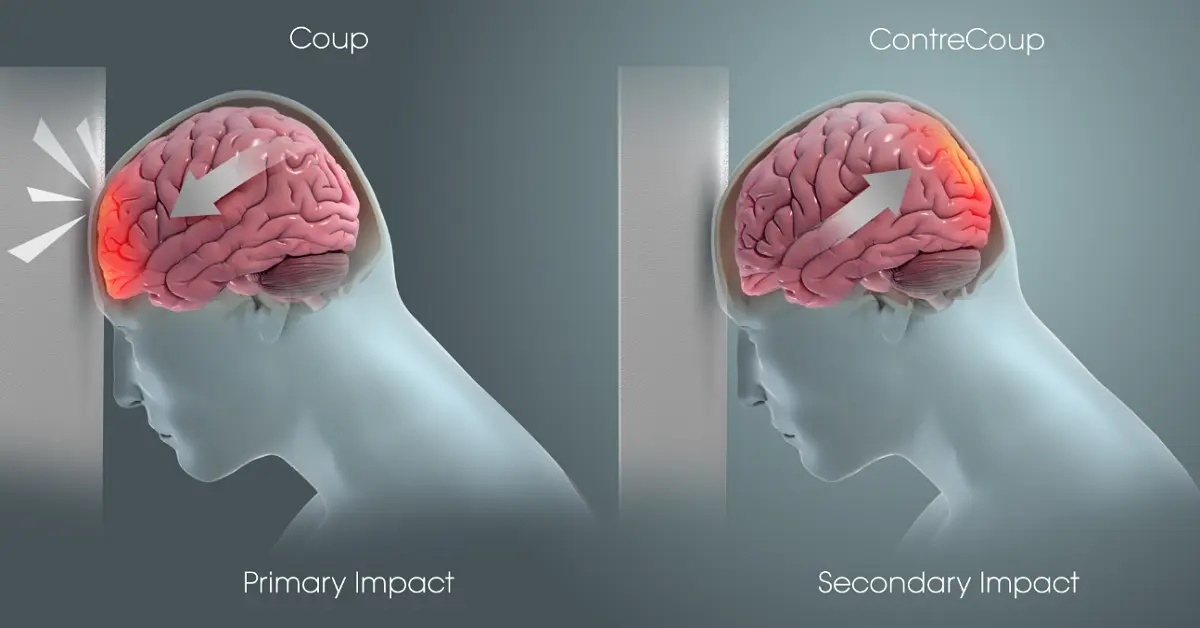
1. Introduction to Brain Injuries
Brain injuries are complex medical conditions that can range from mild concussions to severe traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) and non-traumatic causes like strokes or oxygen deprivation. Brain injuries often lead to a disruption in the brain’s normal functioning, causing physical, cognitive, and emotional impairments.
They can result from several causes, including accidents, assaults, falls, or even medical complications. The severity and type of what caused sean’s brain injury? determine the impact on an individual’s life, and in some cases, it can be life-altering or fatal. Early diagnosis and intervention are key to preventing further complications and promoting recovery.
2. Sean’s Story: The Beginning
Sean’s journey with his brain injury was sudden and life-changing. Sean, a previously healthy and active individual, experienced a dramatic shift in his life when he suddenly faced neurological symptoms that led to a medical diagnosis of a what caused sean’s brain injury?. But what caused Sean’s brain injury? Delving into his story involves understanding potential factors such as trauma, hypoxia, or even medical negligence.
Initially, Sean’s family noticed subtle changes in his behavior. Gradually, his cognitive functions declined, and he started showing physical symptoms such as difficulty with motor coordination and speech. Concerned, they took him to the hospital where doctors suspected a brain injury. However, diagnosing the exact cause took longer than expected.
3. Types of Brain Injuries
Brain injuries are primarily categorized into traumatic and non-traumatic injuries. Each type presents unique causes, symptoms, and recovery processes.
3.1 Traumatic Brain Injuries (TBI)
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is caused by an external force impacting the head, leading to damage in brain tissue. This force could be a blow, bump, or a jolt that causes the brain to collide with the skull. TBIs are categorized into three types:
- Mild TBI: Commonly referred to as a concussion. Symptoms include temporary confusion, dizziness, and headaches.
- Moderate TBI: This type often results in more severe cognitive and physical impairments. Loss of consciousness lasting from minutes to hours is common.
- Severe TBI: Severe TBIs often result in extended unconsciousness or amnesia. This level of injury can lead to lifelong disabilities or death.
3.2 Non-Traumatic Brain Injuries
Non-traumatic brain injuries, in contrast, result from internal conditions rather than external forces. These include:
- Stroke: When blood supply to the brain is disrupted, causing brain cells to die.
- Infections: Meningitis or encephalitis can lead to brain inflammation, damaging brain tissue.
- Hypoxia or Anoxia: Oxygen deprivation, due to incidents like drowning or cardiac arrest, can cause significant brain damage.
- Tumors: Growths within the brain may exert pressure on surrounding tissues, leading to injury.
For Sean, doctors had to investigate both traumatic and non-traumatic causes to uncover the root of his injury.
4. The Role of Accidents in Brain Injuries
A significant portion of brain injuries result from accidents, which may occur unexpectedly and have immediate or delayed impacts on brain function.
4.1 Vehicular Accidents
One of the leading causes of TBIs is vehicular accidents. Car crashes, motorcycle collisions, or accidents involving pedestrians can result in serious head trauma. In such incidents, the force of impact can cause the brain to hit the inside of the skull, leading to bruising, bleeding, or swelling.
4.2 Sports Injuries
Athletes, especially those involved in contact sports such as football, boxing, and hockey, face a high risk of brain injuries. Repeated blows to the head can lead to chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE), a degenerative brain condition.
4.3 Falls and Slips
Falls are a common cause of brain injuries, especially in older adults and children. Slipping in a bathroom, falling from a height, or simply tripping over an object can lead to significant head trauma, sometimes without immediate symptoms.
5. Medical Misdiagnosis and Sean’s Brain Injury
Medical misdiagnosis is another factor that can exacerbate brain injuries. If a what caused sean’s brain injury? is not promptly or accurately diagnosed, critical treatment may be delayed, leading to worsening symptoms or even permanent damage.
In Sean’s case, early medical reports indicated mild symptoms that didn’t initially raise alarm bells. Unfortunately, this delayed further investigations and treatment. By the time Sean received the correct diagnosis, his condition had progressed, making recovery more challenging.
Misdiagnosis can occur when symptoms mimic other neurological or physical conditions, causing confusion during initial evaluations. This underscores the importance of thorough diagnostic procedures in brain injury cases.
6. Hypoxic and Anoxic Brain Injuries: An Overview
Sean’s brain injury may have been caused by oxygen deprivation, leading to what is known as anoxic or hypoxic brain injury.
Hypoxic Brain Injury
Hypoxia refers to a partial lack of oxygen reaching the brain. While some oxygen is present, it is insufficient to support normal brain function. Common causes include:
- Choking
- Severe asthma attacks
- Carbon monoxide poisoning
Anoxic Brain Injury
Anoxia occurs when the brain is completely deprived of oxygen. This can happen due to incidents like:
- Drowning
- Heart attacks
- Severe blood loss
Both types of oxygen deprivation can lead to widespread brain damage within minutes, causing cognitive and motor impairments.
7. Medical Response: Time-Sensitive Interventions
The immediate response to a brain injury is critical. Whether the cause is trauma or oxygen deprivation, early intervention can prevent further damage. Emergency medical protocols focus on stabilizing the patient’s condition and preventing secondary complications such as brain swelling or internal bleeding.
Emergency Care for Brain Injuries
The key steps in treating brain injuries involve:
- Maintaining oxygen supply: Ensuring the brain gets enough oxygen is vital.
- Reducing brain swelling: This may involve medication or surgery to relieve pressure.
- Monitoring intracranial pressure: Medical teams track brain activity to detect any abnormalities.
Sean’s injury required a swift medical response to prevent worsening symptoms. Emergency care teams had to stabilize him before further tests could determine the exact nature of his injury.
8. Sean’s Treatment Journey
8.1 Initial Medical Response
After Sean’s brain injury was diagnosed, the immediate focus was on preventing any further damage. Doctors administered medications to reduce swelling, control seizures, and maintain adequate blood flow to his brain. The early days were crucial, with Sean being monitored in an intensive care unit (ICU).
8.2 Rehabilitation Efforts
Once Sean’s condition stabilized, he began a long journey of rehabilitation. what caused sean’s brain injury? rehabilitation involves a combination of therapies designed to restore motor, cognitive, and emotional functions.
8.3 Physical Therapy and Cognitive Therapy
Sean underwent intensive physical therapy to regain his mobility and strength. At the same time, he engaged in cognitive therapy to improve memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. While progress was slow, each small victory marked a step forward in his recovery process.
9. Emotional and Psychological Effects of Brain Injuries
9.1 The Emotional Toll on Sean and His Family
Brain injuries don’t just affect the individual; they also impact family members and caregivers. Sean experienced emotional distress, frustration, and a loss of independence as he struggled with his new reality. His family, too, faced challenges as they navigated the complexities of caregiving and coping with uncertainty.
9.2 Psychological Challenges Post-Injury
Psychological effects are common in what caused sean’s brain injury? survivors. Depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can develop, particularly if the injury was caused by a traumatic event. In Sean’s case, dealing with these emotional difficulties became an integral part of his overall treatment plan.
10. Legal and Medical Implications of Brain Injuries
10.1 Medical Negligence
In some cases, brain injuries may occur due to medical negligence. Misdiagnoses, delayed treatment, or surgical errors can lead to severe outcomes. If medical professionals fail to meet the standard of care, legal action may be pursued.
10.2 Legal Actions Taken by Sean
Sean’s family considered legal action after discovering the initial misdiagnosis that delayed his treatment. Seeking compensation for medical costs and future care was necessary to ensure that Sean received the best possible care throughout his recovery.
11. Long-Term Effects of Brain Injuries
Brain injuries often have long-term effects that can last for years, or even a lifetime.
11.1 Physical Impact
The physical effects of brain injuries vary widely depending on the severity of the damage. Sean faced difficulties with motor skills, coordination, and balance. Over time, with therapy, some of these challenges improved, but others remained persistent.
11.2 Cognitive and Mental Health Issues
Memory loss, difficulty concentrating, and problems with reasoning are common cognitive effects that Sean experienced. Additionally, brain injuries can exacerbate mental health problems, requiring ongoing psychological support.
12. Genetic Factors in Brain Injury Recovery
Researchers are increasingly examining the role of genetics in what caused sean’s brain injury? recovery. While treatment protocols remain essential, genetic predispositions may influence how well an individual recovers from a brain injury. Some people may be genetically more resilient to brain damage, while others may face greater challenges.
13. Advancements in Brain Injury Treatment
The field of brain injury treatment has seen significant advancements in recent years. From improved diagnostic techniques like advanced neuroimaging to innovative rehabilitation therapies, modern medicine is better equipped to help individuals like Sean recover.
New treatments include:
- Stem cell therapy to regenerate damaged brain tissue.
- Virtual reality therapy to aid in cognitive rehabilitation.
- Neuroplasticity training to help the brain rewire and adapt.
14. Raising Awareness: How Sean’s Story Contributed
Sean’s story has become a beacon of awareness for brain injuries. His family has used his experience to raise awareness about the importance of early diagnosis, the complexities of brain injury recovery, and the need for improved medical protocols. Sean’s journey has inspired others facing similar challenges and has helped shine a light on this often-overlooked issue.